Hajer Kilani
Conference 2024 Poster
Poster Title
Description of Bacteremia in a Tunisian Orthopedic Institute: Epidemiology and Antibiotic Resistance Profile
Authors and Affiliations
Hajer Kilani1,3, Salma Kaoual1,2 , Fatma Kaabi1, Eya Samaali1,Sophia Bouhalila Besbes1,2
1Microbiology Unit, Clinical Biology Laboratory, Mohamed Kassab Institute of Orthopedics, Tunis, Tunisia
2Faculty of Pharmacy, Department of Biology B, University of Monastir, Monastir, Tunisia
3Faculty of Medicine, LR99ES09 Laboratory of Antibiotic Resistance, University of Tunis El Manar, Tunis, Tunisia
Abstract
Background
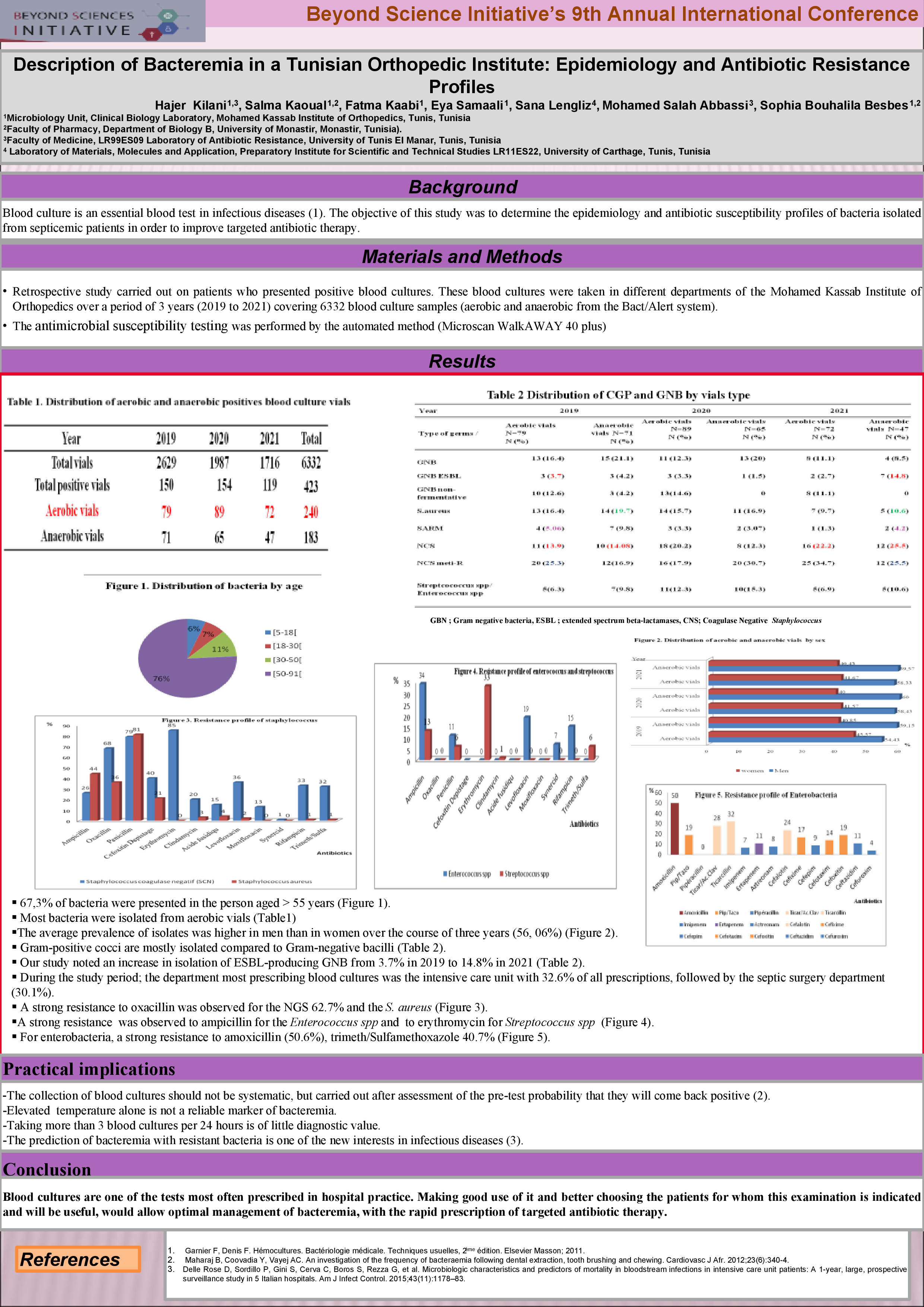
Blood cultures are the cornerstone of the microbiological diagnosis of bacteremia. The objective of our study is to determine the epidemiology and antibiotic susceptibility profile of bacteria isolated from blood cultures, in order to optimize probabilistic antibiotic therapy and improve targeted antibiotic therapy. This article aims to summarize the main predictions that we can draw when it comes to evaluate the utility of collecting a blood culture.
Methods
Retrospective study carried out on patients who presented positive blood cultures. These blood cultures were taken in different departments of the Mohamed Kassab Institute of Orthopedics over a period of 3 years (from 2019 until 2021). Duplicates have been excluded. involvingblood culture samples (aerobic and anaerobic from the Bact/Alert system). The antibiogram was performed by the automated method (Microscan WalkAWAY 40 plus).
Results
Among 6332 we isolated 420 germs which represent 18.5 % of positive blood culture vials with a contamination of 15% of the total blood culture vials. The Gram-positive cocci (GPC) were mostly isolated with 70.4% compared to Gram-negative bacilli (GNB) (29.6%). The average prevalence of strains was higher in men than in women over the course of three years (56%). The sex ratio was 0.7 for aerobic vials and 0.6 anaerobic vials. The department most prescribing blood cultures was the intensive care unit with 32.6% of all prescriptions.We found that 67,3% of bacteria were presented in the person aged > 55 years. Escherichia coli is the species most frequently BGN isolated in positive blood cultures (22.4%).For the CGP a strong resistance to oxacillin was observed for the SCN 62.7% and the S.aureus 30.3%. For enterobacterial we noticed a strong resistance to amoxicillin (50.6%. We noted an increase in isolation of ESBL-producing GNB from 3.7% in 2019 to 14.8% in 2021
Conclusions
Rigorous surveillance of resistance rate is necessary to determine appropriate empirical treatment and limit the spread of multiresistant strains in North Africa.

Leave A Comment