Ovinuchi P Ejiohuo
Conference 2023 Presentation
Project title
Electrospun polyphenols in wound healing with improved antimicrobial activity – the review of current literature
Authors and Affiliations
Ovinuchi Ejiohuo 1, Magdalena Paczkowska-Walendowska 1, Judyta Cielecka-Piontek 1
1. Department of Pharmacognosy, Poznan University of Medical Sciences, Poznan, Poland
Abstract
Background
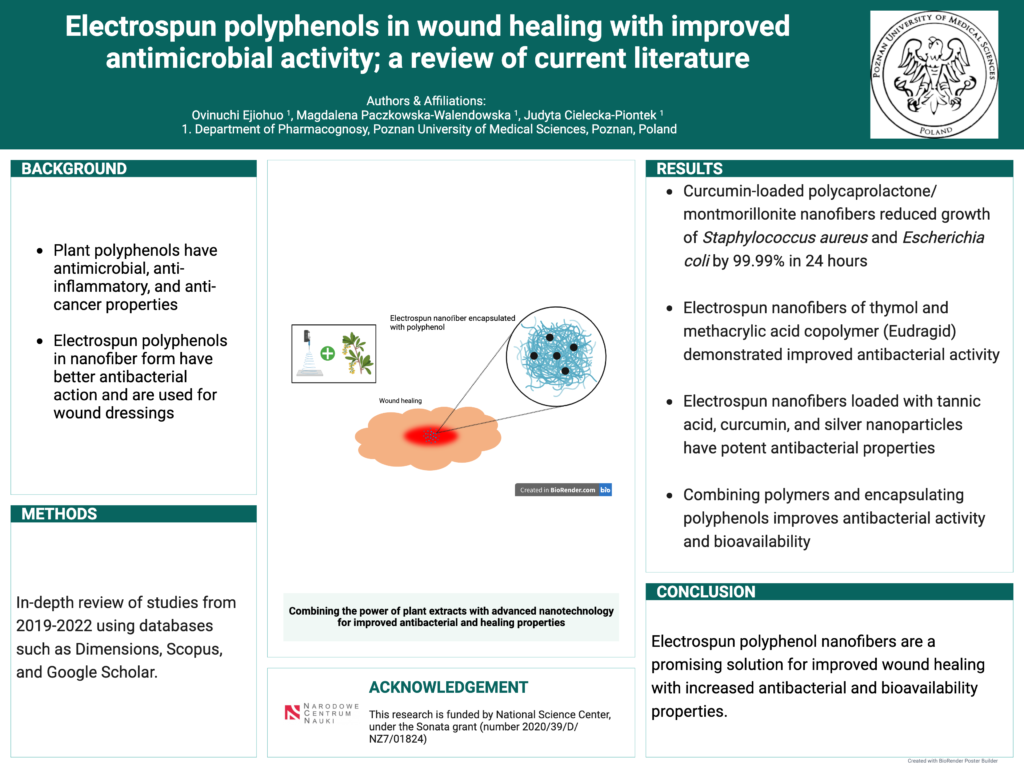
Plant polyphenols are biologically active substances with antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer properties. For this reason, polyphenols are good compounds to use in wound healing. The introduction of polyphenols into the fiber structure allows for better use of their activity, especially those in the field of anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties. In addition, the introduction of polyphenols into the fiber structure may have a positive effect on improving their functionality in the treatment of wounds.
Methods
To conduct an in-depth review, databases including Dimensions, Scopus, and Google Scholar were used. Studies completed between 2019 and 2022 were given more weight to ensure analysis of contemporary methods and conclusions. The work included a substantive review of 59 papers. This study was part of the implementation of tasks for the Sonata project (Mucoadhesive delivery systems of polyphenols as an effective way to increase their health-promoting properties) from the National Science Center grant (number 2020/39/D/NZ7/01824).
Results
The most important results, reported in experimental works, confirming the use of polyphenols in fibers in the treatment of wounds are presented below. Curcumin-loaded polycaprolactone/montmorillonite nanofibers were created via electrospinning and outperformed nanofibers without curcumin in terms of antibacterial activity (Sadeghianmaryan et al., 2020). Thymol-encapsulated ethanol-soluble polyurethane combined with fluorinated polyurethane nanofibers in just 24 hours reduced Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli growth by 99.99% (Yue et al., 2021) while the electrospun nanofiber of thymol and methacrylic acid copolymer called Eudragid developed by Miranda-Calderon et al. in 2022 demonstrated improved antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli even at modest release levels.
Conclusions
There is a predilection for combining many polymers to create nanofibers. The antibacterial, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory activity of these polyphenols has been successfully increased by current methods. Improvements have also been made to the nanofiber’s adsorption capacity and capacity to maintain the potency of the polyphenol. Overall, all of these have significantly increased the plant extract’s bioavailability.