Sona Sajeer
Moldova
Determinants of Quality of Life in Patients with Myelodysplastic Syndromes
Sona Sajeer 1,Vasile Musteata2
1.year VI, State university of medicine and pharmacy ‘Nicolae Testimitanu’,Moldova
2 . University Associate Professor, vice head for education, department of Oncology, Hematology and Radiotherapy USMF
Abstract
Background
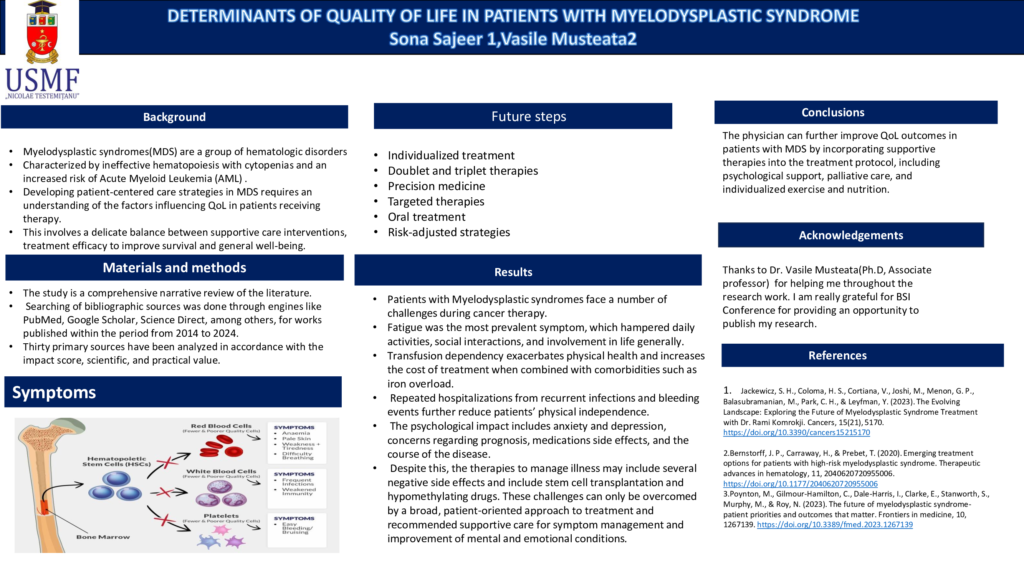
Myelodysplastic syndromes(MDS) are a group of hematologic disorders characterized by ineffective hematopoiesis, presenting with cytopenias and an increased risk of Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) . Major symptoms such as anemia, weakness, infections and bleeding tendencies are common in MDS patients and will lower their Quality of Life(QoL) . Developing patient-centered care strategies in MDS requires an understanding of the factors influencing QoL in patients receiving therapy. This will involve a delicate balance between supportive care interventions, treatment efficacy to improve survival and general well-being.
Methods
The study is a comprehensive narrative review of the literature. Searching of bibliographic sources was done through engines like PubMed, Google Scholar, Science Direct, among others, for works published within the period from 2014 to 2024. Thirty primary sources have been analyzed in accordance with the impact score, scientific, and practical value.
Results
Patients with Myelodysplastic syndromes face a number of challenges during cancer therapy. Fatigue was the most prevalent symptom, which hampered daily activities, social interactions, and involvement in life generally. Transfusion dependency exacerbates physical health and increases the cost of treatment when combined with comorbidities such as iron overload. Repeated hospitalizations from recurrent infections and bleeding events further reduce patients’ physical independence. The psychological impact includes anxiety and depression, concerns regarding prognosis, medications side effects, and the course of the disease. Despite this, the therapies to manage illness may include several negative side effects and include stem cell transplantation and hypomethylating drugs. These challenges can only be overcomed by a broad, patient-oriented approach to treatment and recommended supportive care for symptom management and improvement of mental and emotional conditions.
Conclusions
The physician can further improve QoL outcomes in patients with MDS by incorporating supportive therapies into the treatment protocol, including psychological support, palliative care, and individualized exercise and nutrition.

Leave A Comment