Samah Kotb Nasr Eldeen
Egypt
Knockdown of CD-74 in the Proliferative and Apoptotic Activity of Breast Cancer Cells
Hussain Al Ssadh1, Waleed Al Abdulmonem2*, Zafar Rasheed3, Inamul Hasan Madar4, Jamila Alhoderi1, Samah K. Nasr Eldeen 5,6, Ali Alradhwan7, Noura Alasmael8, Abdullah Alkhamiss2, Nelson Fernández1
1School of Biological Sciences, University of Essex, Colchester, UK; 2Department of Pathology, College of Medicine, Qassim University, Qassim, Saudi Arabia; 3Department of Medical Biochemistry, College of Medicine, Qassim University, Saudi Arabia; 4Department of Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering, Bharathidasan University, Tiruchirappalli, India; 5Clinical Laboratory Sciences, Inaya Medical College, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia; 6Central Laboratories, Egyptian Ministry of Health, Tanta, Egypt; 7Biochemistry Department, College of Medicine, Imam Abdulrahman Bin Faisal University, Saudi Arabia; 8College of Medicine, King Saud University, Saudi Arabia
Abstract
Background
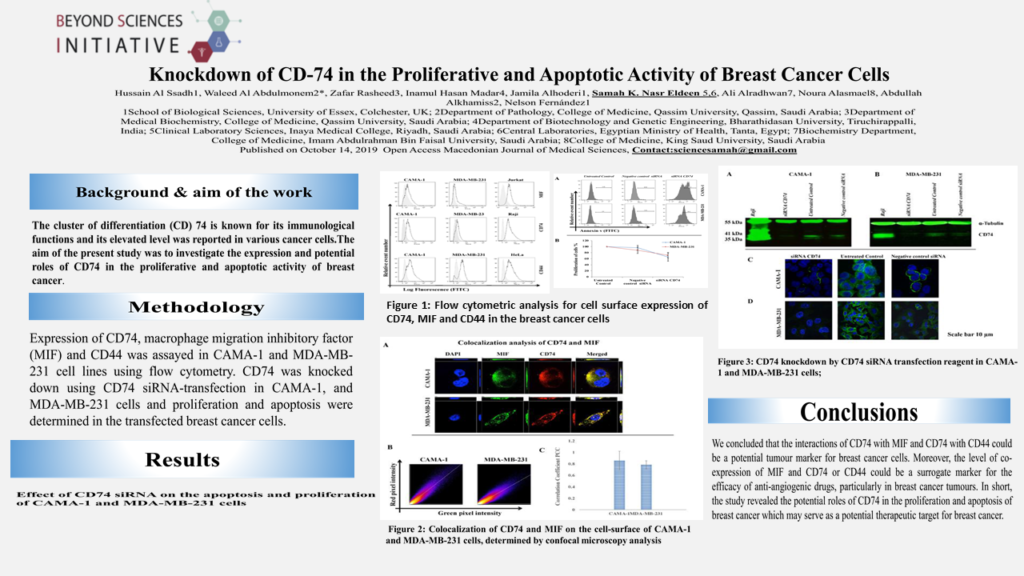
The cluster of differentiation (CD) 74 is known for its immunological functions and its elevated level was reported in various cancer cells.
The aim of the present study was to investigate the expression and potential roles of CD74 in the proliferative and apoptotic activity of breast cancer.
Methods
Expression of CD74, macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) and CD44 was assayed in CAMA-1 and MDA-MB-231 cell lines using flow cytometry.
CD74 was knocked down using CD74 siRNA-transfection in CAMA-1, and MDA-MB-231 cells and proliferation and apoptosis were determined in the transfected breast cancer cells.
Results
The data showed that CD74, MIF and CD44 were expressed in breast cancer cell lines and were associated with cell proliferation and apoptosis. Correlation analysis revealed that CD74 was positively correlated and colocalised with MIF on the cell-surface of CAMA-1 and MDA-MB-231. The knockdown of CD74 significantly reduced CAMA-1 and MDA-MB-231 cell proliferation and increased the level of apoptotic cells.
Conclusions
In conclusion, it was observed that the interaction of MIF with CD74 CD44 could be a potential tumor marker for breast cancer cells. Moreover, level of co-expression of MIF and CD74 could be a surrogate marker for the efficacy of anti-angiogenic drugs, particularly in breast cancer tumors. Also, knockdown of CD74 by CD74 siRNA significantly reduced CAMA-1 and MDA-MB-231 cell proliferation and increased the level of apoptotic cells.

Leave A Comment