Aneta Ostróżka-Cieślik
Poland
Investigation of thermosensitive insulin hydrogels in the context of supporting chronic wound treatment
Aneta Ostróżka-Cieślik, Marcin Przybyła, Barbara Dolińska
Department of Pharmaceutical Technology, Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences in Sosnowiec, Medical University of Silesia, Jedności Street 8b, 41-208 Sosnowiec, Poland
Abstract
Background
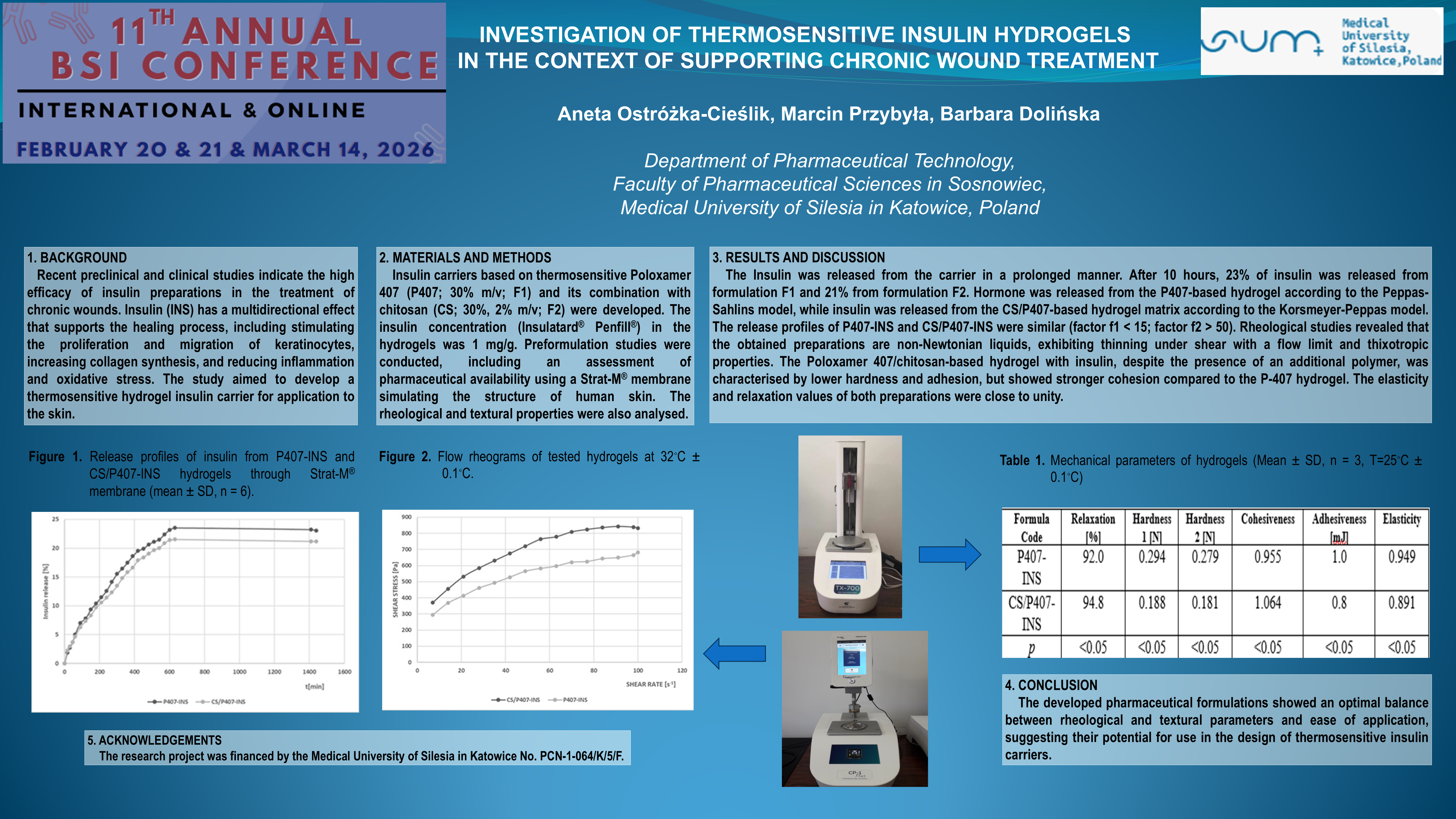
BACKGROUND: Recent preclinical and clinical studies indicate the high efficacy of insulin preparations in the treatment of chronic wounds. Insulin (INS) has a multidirectional effect that supports the healing process, including stimulating the proliferation and migration of keratinocytes, increasing collagen synthesis, and reducing inflammation and oxidative stress. The study aimed to develop a thermosensitive hydrogel insulin carrier for application to the skin.
Methods
METHODS: Insulin carriers based on thermosensitive Poloxamer 407 (P407; 30% m/v; F1) and its combination with chitosan (CS; 30%, 2% m/v; F2) were developed. The insulin concentration (Insulatard® Penfill®) in the hydrogels was 1 mg/g. Preformulation studies were conducted, including an assessment of pharmaceutical availability using a Strat-M® membrane simulating the structure of human skin. The rheological and textural properties were also analysed.
Results
RESULTS: Insulin was released from the carrier in a prolonged manner. After 10 hours, 23% of insulin was released from formulation F1 and 21% from formulation F2. Hormone was released from the P407-based hydrogel according to the Peppas-Sahlins model, while insulin was released from the CS/P407-based hydrogel matrix according to the Korsmeyer-Peppas model. The release profiles of P407-INS and CS/P407-INS were similar (factor f1 < 15; factor f2 > 50). Rheological studies revealed that the obtained preparations are non-Newtonian liquids, exhibiting thinning under shear and thixotropic properties. The Poloxamer 407/chitosan-based hydrogel with insulin, despite the presence of an additional polymer, was characterised by lower hardness and adhesion, but showed stronger cohesion compared to the P407 hydrogel. The elasticity and relaxation values of both preparations were close to unity.
Conclusions
CONCLUSIONS: The developed pharmaceutical formulations showed an optimal balance between rheological and textural parameters and ease of application, suggesting their potential for use in the design of thermosensitive insulin carriers.

Leave A Comment