Shorouk El Sayed
Egypt
Quercetin Nanoliposome therapy ameliorates hepatic damage induced by Co-Amox treatment: Gut-liver axis.
Mahran Mohamed Abd El-Emam 1,*[M4.1],[M5.1] Mahmoud Mostafa 2, Amina A. Farag 3, Heba S. Youssef 4, Azza S. El-Demerdash 5, Heba Bayoumi 6, Mohammed A. Gebba 7,8, Sawsan M. El-Halawani 9, Abdulrahman M. Saleh 10, Amira M. Badr 11,* and Shorouk El Sayed 12
1. Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Zagazig University, Zagazig 44511, Egypt, 2. Department of Pharmaceutics, Faculty of Pharmacy, Minia University, Minia 61519, Egypt; 3. Department of Forensic Medicine and Clinical Toxicology, Faculty of Medicine, Benha University, Banha. 4. Department of Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, Benha University, Benha 13518, Egypt; 5. Microbiology Department, Zagazig Branch, Animal Health Research Institute (AHRI), Agriculture Research Centre (ARC), Zagazig; 6. Department of Histology and Cell Biology, Faculty of Medicine, Benha University, Benha 13518, Egypt; 7. Department of Anatomy and Embryology, Faculty of Medicine, Benha University, Benha 13518, Egypt; 8. Department of Anatomy and Embryology, Faculty of Medicine, Merit University, Sohag 82524, Egypt; 9. Department of Biotechnology, Urology and Nephrology Center, Mansoura University, 10. Pharmaceutical Medicinal Chemistry & Drug Design Department, Faculty of Pharmacy, Al-Azhar University, Cairo 11884, Egypt; 11. Pharmacology and Toxicology Department, Faculty of Pharmacy, King Saud University; 12. Department of Microbiology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Zagazig University, Zagazig 44511, Egypt;
Abstract
Background
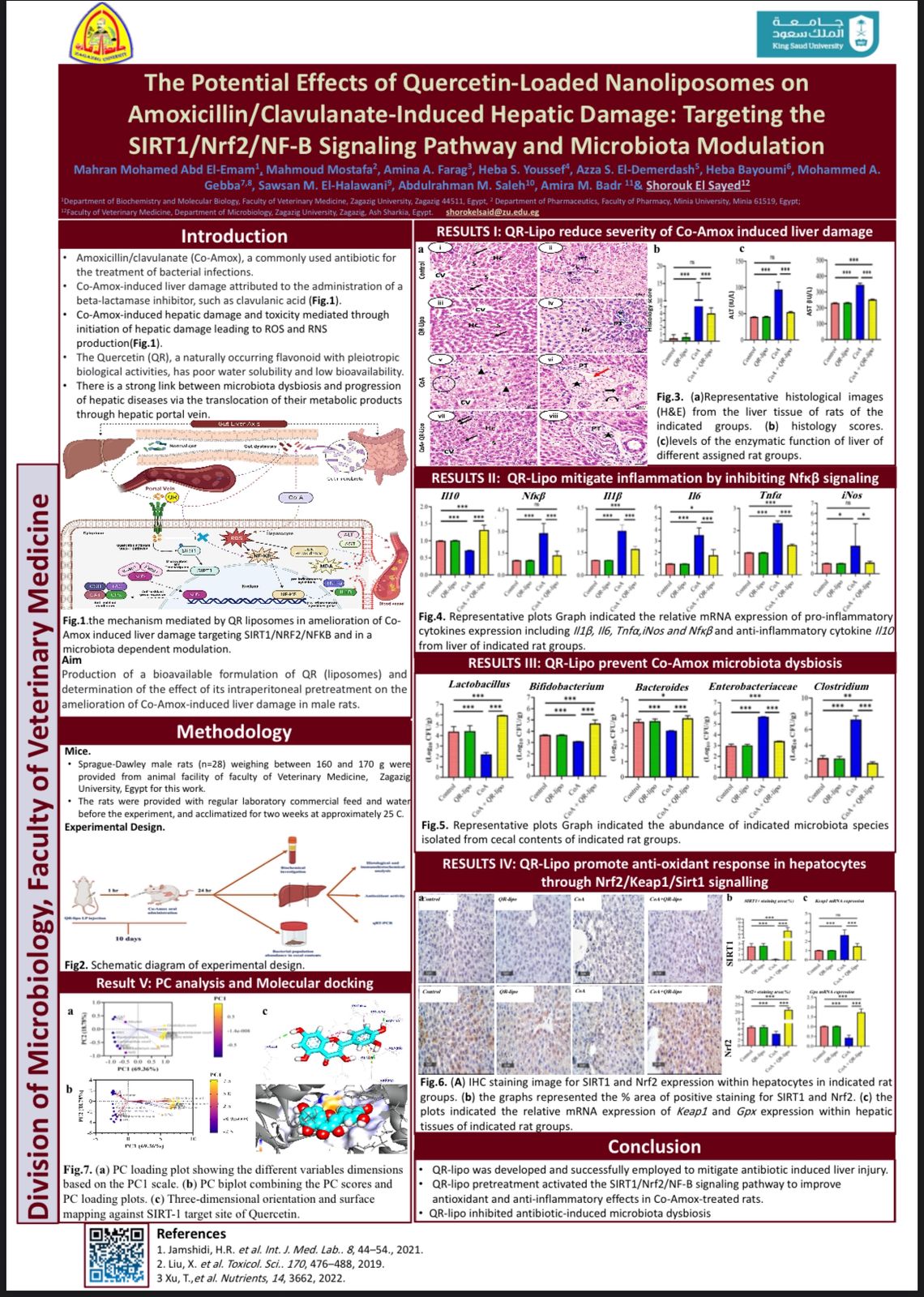
Amoxicillin/clavulanate (Co-Amox), a commonly used antibiotic for the treatment of
bacterial infections, has been associated with drug-induced liver damage specially due to haphazard use of antibiotic for pediatrics in Egypt. Quercetin (QR), a naturally occurring flavonoid with pleiotropic biological activities, has poor water solubility and low bioavailability. The objective of this work was to produce a more bioavailable formulation of QR (liposomes) and to determine the effect of its intraperitoneal pretreatment on the amelioration of Co-Amox-induced liver damage in male rats. Four groups of rats were defined: control, QR liposomes (QR-lipo), Co-Amox, and Co-Amox and QR-lipo. Liver injury severity in rats was evaluated for all groups through measurement of serum liver enzymes, liver antioxidant status, proinflammatory mediators, and microbiota modulation.
Methods
Rats were randomly allocated into four groups (n = 7), control group, quercetin
liposome-treated group (QR-lipo), the Co-Amox treated group, and the Co-Amox group
treated with QR-lipo (Co-Amox and QR-lipo). The liver injury was induced by Co-Amox
oral suspension at a dose of 60 mg/kg for ten consecutive days [8]. Rats in the Co-Amox
and QR-lipo group received daily doses of 5 mg/kg of QR-lipo intraperitoneally for
10 consecutive days, 1 h before receiving an oral suspension of Co-Amox [37]. Then blood, liver and fecal samples were collected for evaluation using H&E, PCR, 16 S for microbiota
Results
The results revealed that QR-lipo reduced the severity of Co-Amox-induced hepatic damage in rats, as indicated by a reduction in serum liver enzymes and total liver antioxidant capacity. In addition, QR-lipo upregulated antioxidant transcription factors SIRT1 and Nrf2 and downregulated liver proinflammatory signatures, including IL-6, IL-1, TNF-a, NF-kB, and iNOS, with upregulation in the anti-inflammatory one, IL10. QR-lipo also prevented Co-Amox-induced gut dysbiosis by favoring the colonization of Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, and Bacteroides over Clostridium and Enterobacteriaceae. These results suggested that QR-lipo ameliorates Co-Amox-induced liver damage by targeting SIRT1/Nrf2/NF-B and modulating the microbiota.
Conclusions
QR-lipo was developed and successfully employed to mitigate antibiotic induced liver injury.
QR-lipo pretreatment activated the SIRT1/Nrf2/NF-B signaling pathway to improve antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects in Co-Amox-treated rats.
QR-lipo inhibited antibiotic-induced microbiota dysbiosis.

Leave A Comment