Mulugeta Bekele
Ethiopia
AI-driven global health framework integrating multi-omics, distributed data, and geospatial analytics for precision disease diagnostics & surveillance
Mulugeta Tilahun Bekele1, University of Gondar
Abstract
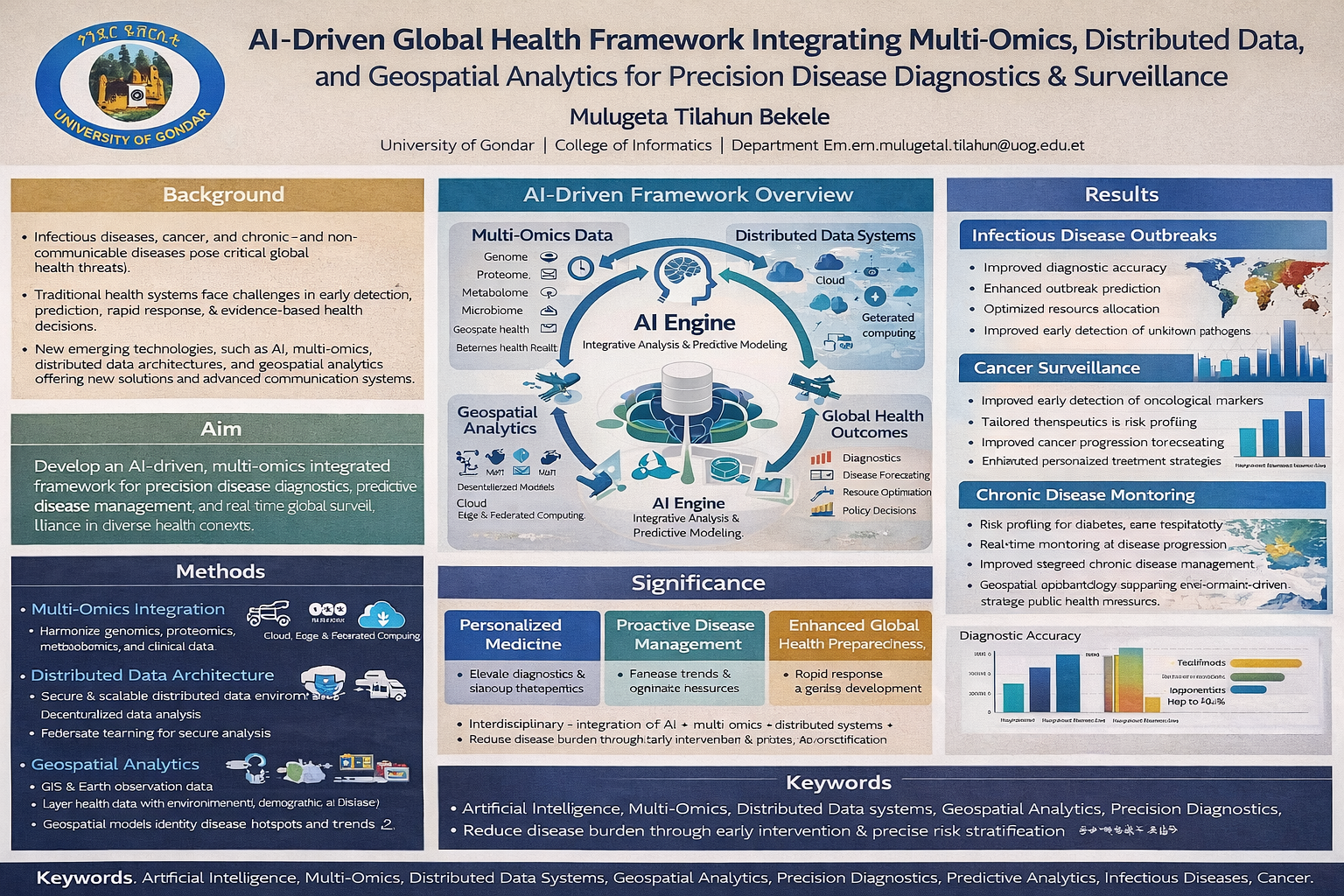
Background
The increasing prevalence and complexity of infectious diseases, cancer, and chronic non-communicable diseases necessitate innovative, technology-driven solutions for global health intelligence. Current healthcare systems face challenges in early detection, predictive management, and real-time disease surveillance. Emerging technologies such as AI, multi-omics integration, distributed computing, geospatial analytics, and advanced communication systems offer unprecedented opportunities to address these challenges.
Methods
This research proposes a next-generation AI-driven computational and biotechnological framework that integrates multi-omics data, distributed health data architectures, geospatial analytics, and advanced communication technologies. Genomic, proteomic, metabolomic, and clinical datasets are harmonized within distributed computing environments to enable predictive modeling, early detection of disease trends, and identification of personalized therapeutic targets. Geospatial analytics are applied to contextualize health data within environmental, demographic, and socio-economic landscapes. Advanced communication networks support real-time data sharing and collaborative decision-making across healthcare systems and public health authorities.
Results
Validation through case studies—including infectious outbreaks, oncological surveillance, and chronic disease monitoring—demonstrated the framework’s ability to:
Improve diagnostic accuracy
Forecast disease progression
Optimize resource allocation
Support evidence-based health policy decisions
The framework’s interdisciplinary design bridges AI, biotechnology, bioinformatics, geospatial sciences, and distributed systems engineering, producing a scalable and adaptive global health intelligence platform.
Conclusions
Integrating emerging technologies into a unified system has transformative potential for personalized medicine, proactive disease management, and global health preparedness. The framework can reduce disease burden, enhance health system responsiveness, and inform strategic interventions at population and policy levels, representing a significant advancement in AI-driven multi-omics and geospatial intelligence for comprehensive global disease surveillance and management.

Leave A Comment