Abdel Amide Gbadamassi
Morocco
Contribution of hybrid SPECT/CT imaging with 99mTc HMDP in febrile osteoarticular pain
AA. Gbadamassi, H. Bensimimou, H. Batani, Z. Ouassafrar, A. Guensi
Nuclear Medicine Department, Ibn Rochd University Hospital, Casablanca, Morocco
Abstract
Background
Osteoarticular infections constitute a diagnostic and therapeutic emergency, as any delay in management can compromise functional prognosis. Despite advances in imaging, early diagnosis often remains challenging. Owing to its high sensitivity and improved specificity, bone scintigraphy helps guide the diagnosis while precisely identifying the topography of the infectious process. This leads to faster and more appropriate patient management, while significantly reducing both the cost and duration of treatment.
The objective of this study was to demonstrate the contribution of bone scintigraphy in evaluating febrile osteoarticular pain.
Methods
This was a retrospective descriptive and analytical study conducted over a 4-year period in the Nuclear Medicine Department of Ibn Rochd University Hospital in Casablanca. Included were patients presenting with a temperature ≥ 38°C associated with osteoarticular pain who underwent 99mTc-HMDP bone scintigraphy. The chi-square test was used to assess the association between CRP levels and the number of infectious sites.
Results
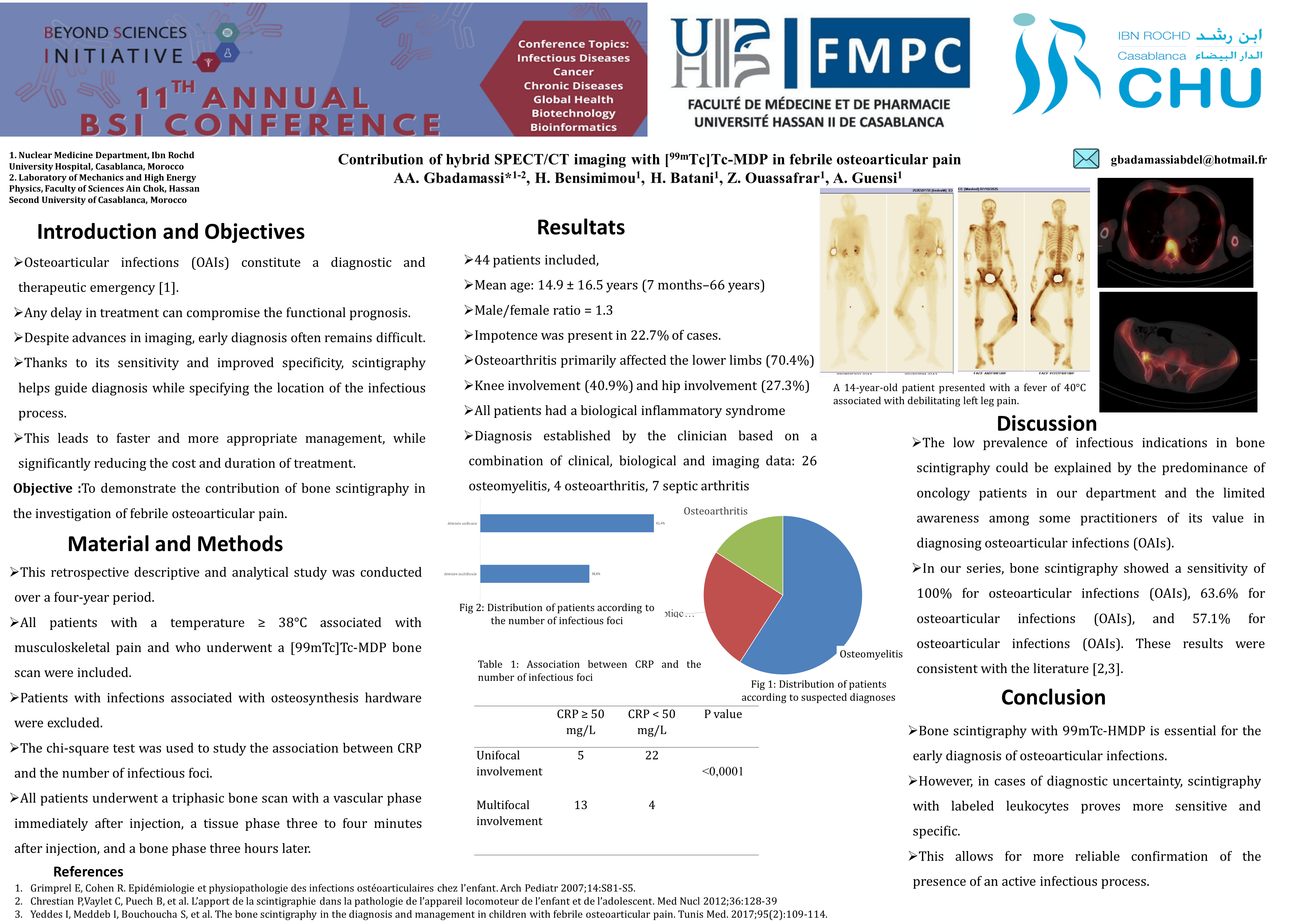
A total of 44 patients were included. The mean age was 14.9 ± 16.5 years (range: 7 months–66 years). Males predominated (54.5%). A portal of entry was identified in 15.9% of cases, and trauma was reported in 13.6%. Functional impairment was present in 22.7% of patients. Osteoarticular infections mainly involved the lower limbs (70.4%), particularly the knee (40.9%) and hip (27.3%). 99mTc-HMDP bone scintigraphy suggested 26 cases of osteomyelitis, 11 osteoarthritis infections, and 7 osteitis. Patients with moderate to severe CRP elevations presented with multifocal involvement. This correlation was statistically significant (p < 0.001), suggesting that a high CRP level could be a relevant indicator of the extent of the infectious process. The final diagnoses established by clinicians based on combined clinical, biological, and imaging findings were: 26 osteomyelitis, 4 septic arthritis, and 7 osteitis. Conclusions 99mTc-HMDP bone scintigraphy is essential for the early diagnosis of osteoarticular infections. However, in cases of diagnostic uncertainty, labeled leukocyte scintigraphy offers higher sensitivity and specificity, thereby confirming the presence of active infectious processes with greater reliability.

Leave A Comment