Conference 2021 Poster Presentation
Project title
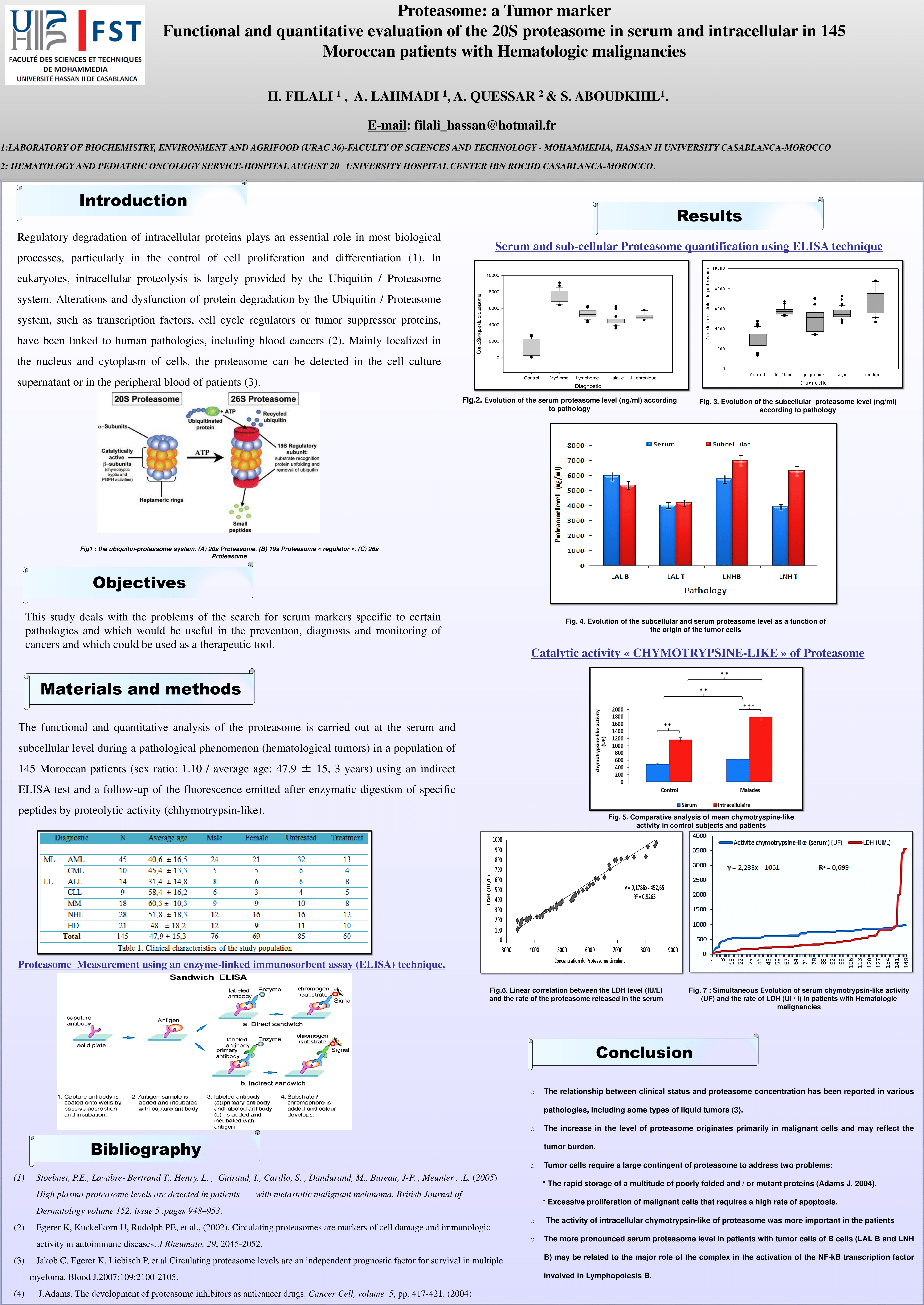
Proteasome: a Tumor marker – Functional and quantitative evaluation of the 20S proteasome in serum and intracellular in 145 Moroccan patients with Hematologic malignancies
Authors and Affiliations
Hassan Filali1,Asmaa Quessar2, Souad Aboudkhil1
1. Laboratory of Biochemistry, Environment and Agrifood (URAC 36), Faculty of Science and Technology Mohammedia, University Hassan II of Casablanca, Morocco
2. Hematology and Pediatric Oncology Service-Hospital August 20, University Hospital Center Ibn Rochd, Casablanca, Morocco
Abstract
Background
In addition to important role in the degradation of abnormal proteins, Proteasome system is an essential player in the regulated degradation of intracellular proteins and directly implicated in the control and regulation of in most biological processes, especially in the control of: transcription, Cell cycle, apoptosis, cell signaling, antigen presentation, inflammation and all aspects of the cellular metabolic networks including physiological or pathological conditions. The clinical success of bortezomib, a 20S proteasome inhibitor, has demonstrated the therapeutic value of inhibiting the proteasome in the fight against cancer.
Methods
Quantitative and functional analysis of the proteasome was conducted at the subcellular level and serum during a pathological phenomenon in 145 Moroccan patients (sex ratio: 1.10 / average age: 47.9 ± 15.3 years) with ELISA assay, and by following the fluorescence emitted after enzymatic digestion of specific peptides by the chymotrypsin-like activity. This work focused on a study in a large cohort of patients with Moroccan Hematologic malignancies in order to follow the evolution of the 20S proteasome in serum and intracellular according to clinical status.
Results
A constitutively increased proteasome activity has been found in myeloma cells. Serum proteasome concentrations were significantly elevated in MM compared with controls (P<0.001). In patients with active MM, there was a significant (P<0.001) decrease from pretreatment to post-treatment proteasome concentrations in responders to chemotherapy.the entire population of 60 patients reported a significant drop in the rate and the activity of the proteasome in serum and intracellular level. The evolutionary trend of subcellular proteasome is significantly linked to the rate of chymotrypsin-like activity.
Conclusions
The use of proteasome circulating assay as a biomarker of tumor and a tool that could be very satisfying to follow patients after remission to prevent a possible fall. Intracellular dosage proteasome reveals important because it allows estimating the predictive score of the risk of toxicity.