Conference 2021 Poster Presentation
Project title
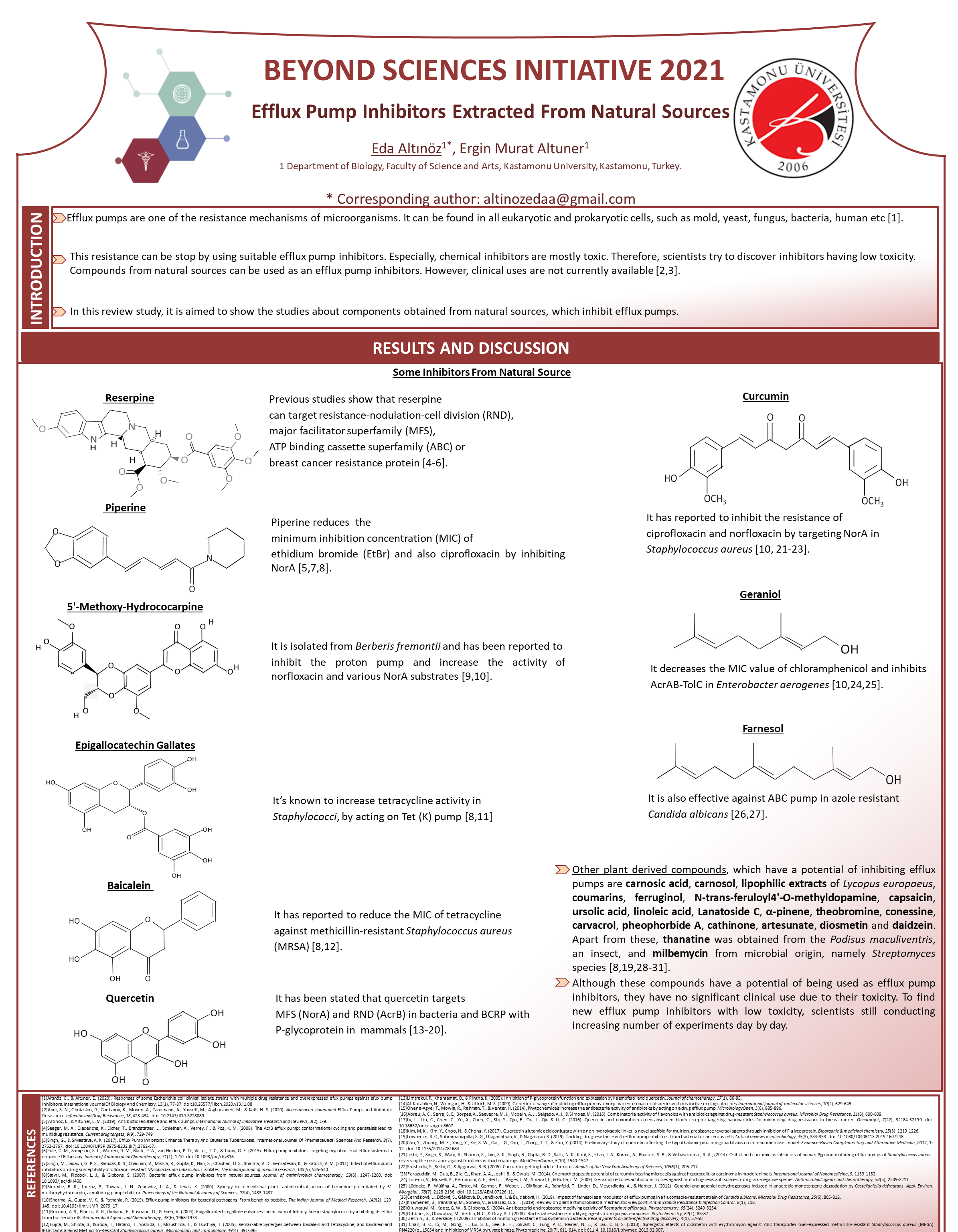
Efflux Pump Inhibitors Extracted from Natural Sources
Authors and Affiliations
Eda Altinöz1, Ergin Murat Altuner1
1. Department of Biology, University of Kastamonu, Kastamonu, Turkey
Abstract
Background
Inhibition of efflux pumps, one of the resistance mechanisms can be achieved by using suitable efflux pump inhibitors. However, the inhibitors are mostly toxic. Therefore, scientists try to discover inhibitors having low toxicity. In this review study, it is aimed to show the studies about components obtained from natural sources, which inhibit efflux pumps.
Methods
Results
Previous studies show that reserpine can target resistance-nodulation-cell division (RND), major facilitator superfamily (MFS), ATP binding cassette superfamily (ABC) or breast cancer resistance protein. Also it was proposed that piperine reduces the minimum inhibition concentration (MIC) of ethidium bromide and also ciprofiloxacin by inhibiting NorA. 5′-methoxy-hydrococarpine isolated from Berberis fremontii has been reported to inhibit the proton pump and increase the activity of norfloxacin and various NorA substrates. Epigallocatechin gallates are known to increase tetracycline activity in Staphylococci, by acting on Tet (K) pump. Baicalein has been reported to reduce the MIC of tetracycline against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Geraniol decreases the MIC value of chloramphenicol and inhibits AcrAB-TolC in Enterobacter aerogenes. Curcumin has been reported to inhibit the resistance of ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin by targeting NorA in S. aureus. Farnesol is also effective against ABC pump in azole resistant Candida albicans. It has been stated that quercetin targets MFS (NorA) and RND (AcrB) in bacteria and BCRP with P-glycoprotein in mammals. Other plant derived compounds, which have a potential of inhibiting efflux pumps are carnosic acid, carnosol, lipophilic extracts of Lycopus europaeus, coumarins, ferruginol, N-trans-feruloyl4′-O-methyldopamine, capsaicin, ursolic acid, linoleic acid, Lanatoside C, α-pinene, theobromine, conessine, carvacrol, pheophorbide A, cathinone, artesunate, diosmetin and daidzein. Apart from these, thanatine was obtained from the Podisus maculiventris, an insect, and milbemycin from microbial origin, namely Streptomyces species.
Conclusions
Although these compounds have a potential of using as efflux pump inhibitors, they have no significant clinical use due to their toxicity. To find new efflux pump inhibitors with low toxicity, scientists still conducting increasing number of experiments day by day.