Conference 2021 Poster Presentation
Project title
In vitro antidiabetes and free radical scavenging activity of Hyptis spicigera
Authors and Affiliations
Ishaq, A.N.1, and Ibrahim, R.1
1. Department of biochemistry, kwara state university, Malete, Nigeria
Abstract
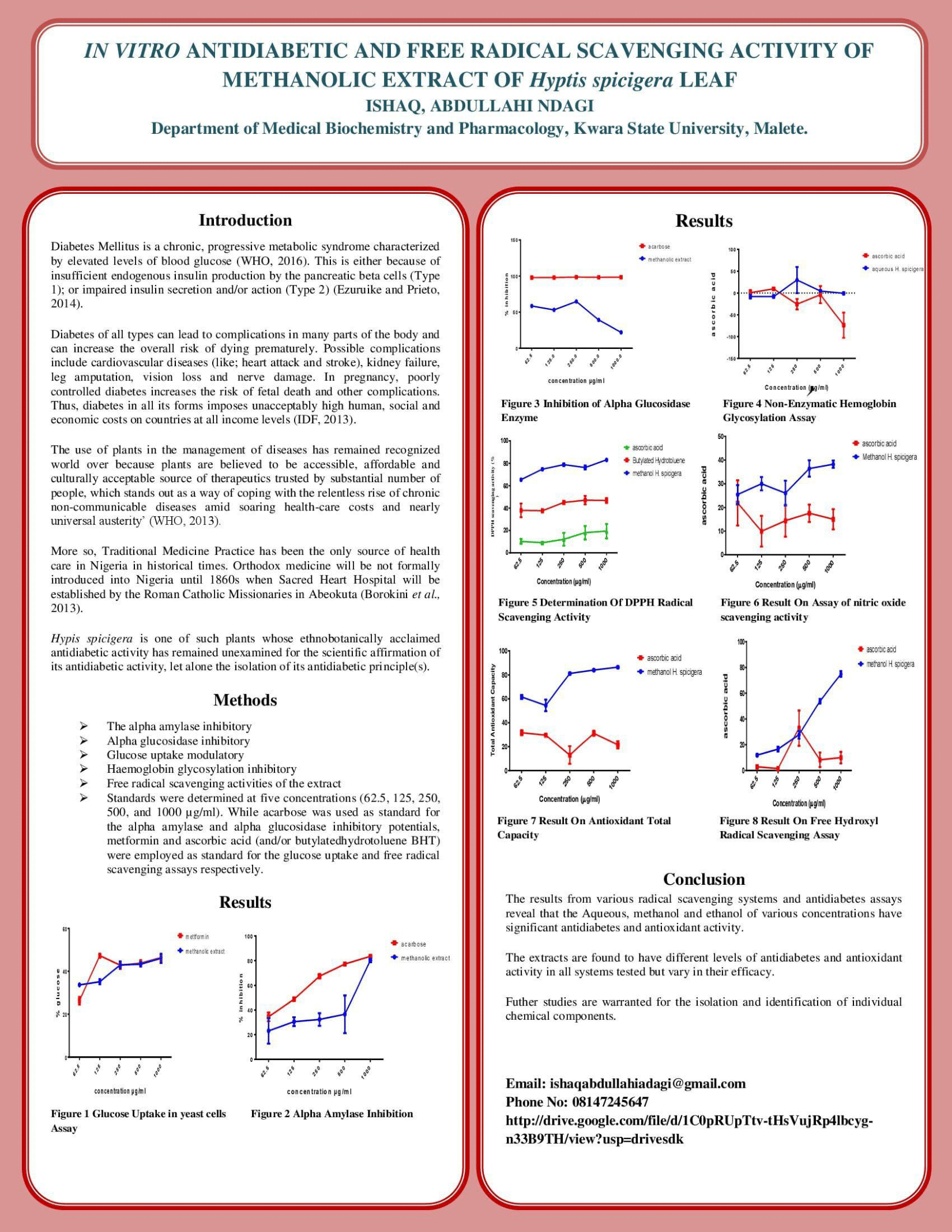
Background
Hyptis spicigera is a plant with reported anti-diabetic and antioxidant properties. The aim of this study is to determine the in vitro antidiabetic and free radical potentials of methanolic extract of Hyptis spicigera leaf (HSL). The HSL was obtained fromZone C Area ElekoYangan, Moro Local Government Kwara State, air dried at room temperature, soaked in methanol (1:20) for 48 hours and filtered using whatmann No 1 filter paper. The filtrate was concentrated at 50oC in water bath to obtain the extract.
Methods
The alpha amylase inhibitory, alpha glucosidase inhibitory, glucose uptake modulatory, haemoglobin glycosylation inhibitory and free radical scavenging activities of the extract and standards were determined at five concentrations (62.5, 125, 250, 500, and 1000 µg/ml). While acarbose was used as standard for the alpha amylase and alpha glucosidase inhibitory potentials, metformin and ascorbic acid (and/or butylated hydrotoluene BHT) were employed as standard for the glucose uptake and free radical scavenging assays respectively.
Results
The therapeutic efficacy of the experimental result is appreciable: The effect of the sample (H. spicigera) to inhibit Alpha amylase and Alpha glucosidase, increases according to the increase in concentration and seems more effective compare to the standard (but more elevated than the sample) indicating the required dose for therapeutic effect and stabilization of physiological functions, the effect of the sample (H. spicigera) increases according to the increase in concentration but seems more effective compared to the standard and therefore it is able to scavenge free radicals than the standard (Ascorbic acid and/or butylated hydrotoluene). Hyptis spicigera leaf (HSL). In glucose uptake modulation, the higher the glucose level the lower the efficiency of the sample or standard i.e the lower the glucose the yeast is able to uptake.
Conclusions
Therefore the efficiency increases according to the level of concentration in most cases and some decline to fit in normal physiological states. Which means the studied plant possesses anti-hyperglycemic and antioxidant activities and could be useful in the management of hyperglycemia and oxidative stress.